Shoulder Dislocation. Bankart and Hill Sachs lesions
The shoulder is the most complex and mobile joint in the human body. As a result, it can suffer from a variety of problems. Many of the ailments are caused by inflammation or tearing of the tendon, as well as problems in the rotator cuff or the bone system.
Among the most frequent injuries we can highlight rotator cuff tear, dislocation, frozen shoulder, bursitis, tendonitis and fractures.
Today we want to focus on two of the most common shoulder injuries, especially in sports: the Bankart injury and the Hill Sachs injury.
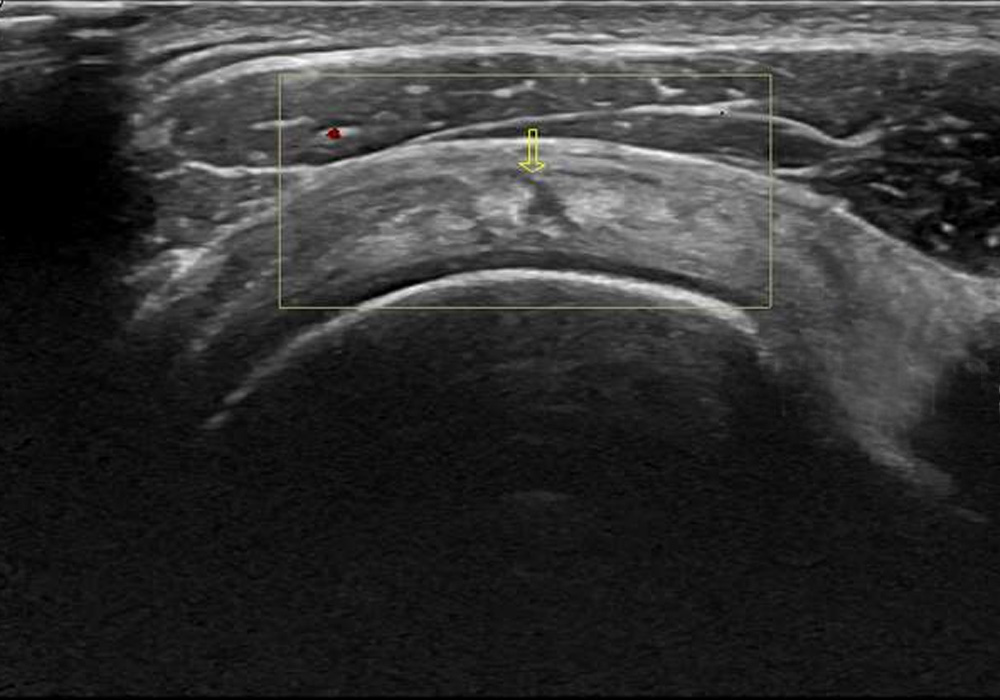
 Bankart lesion involves the rupture of the glenoid labrum which is a fibrous capsule that is located where the head of the humerus sits. It surrounds the base of the shoulder joint and is responsible for giving it greater stability. This usually results from an anterior dislocation of the shoulder, in other words, when the shoulder moves forward, usually due to trauma, the head of the humerus takes the labrum with it, it tears it off.
Bankart lesion involves the rupture of the glenoid labrum which is a fibrous capsule that is located where the head of the humerus sits. It surrounds the base of the shoulder joint and is responsible for giving it greater stability. This usually results from an anterior dislocation of the shoulder, in other words, when the shoulder moves forward, usually due to trauma, the head of the humerus takes the labrum with it, it tears it off.
 Hill Sachs ‘ injury Hill Sachs fracture is a depression of the posterolateral part of the head of the humerus. It is caused by the impaction of the head of the humerus against the glenoid rim. anteroinferior following a traumatic event that causes a dislocation of the shoulder. During shoulder dislocation, the head of the humerus is crushed against the glenoid, depressed, and deformed.
Hill Sachs ‘ injury Hill Sachs fracture is a depression of the posterolateral part of the head of the humerus. It is caused by the impaction of the head of the humerus against the glenoid rim. anteroinferior following a traumatic event that causes a dislocation of the shoulder. During shoulder dislocation, the head of the humerus is crushed against the glenoid, depressed, and deformed.
Symptoms
Patients suffering from Bankart and Hill Sachs lesions experience acute pain and a feeling of shoulder instability. If the lesion is small it may not cause any symptoms, but we will generally find the following symptoms:
- Persistent shoulder pain.
- Instability.
- The patient describes how he feels that “his shoulder is coming out.”
- After the first dislocation, it is common for further episodes of shoulder dislocation to occur.
Treatment
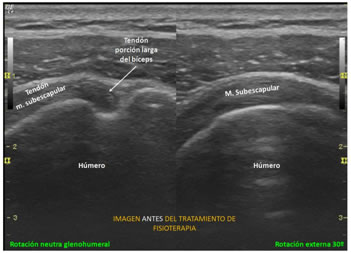
Conservative treatment includes anti-inflammatory drugs, rest, cold application and physical therapy. If this is not sufficient, surgery will be necessary. The patient usually wears a sling for the first week, although it may be necessary for longer.
In most cases, physiotherapy is recommended to help with pain and postoperative sequelae. Physiotherapy treatment will be based on:
- Mobilization of the glenohumeral and scapulothoracic joints mainly in all their ranges of motion.
- Myofascial Treatment.
- Therapeutic massage.
- Analgesic and anti-inflammatory treatment through physical agents such as:
- Shortwave
- Ultrasounds
- Laser
- Analgesic Currents
- Exercise to strengthen the rotator cuff, all the stabilizing muscles of the shoulder and the scapula.
- Scapular control and stabilization exercise.
- Stretching of the shoulder and upper limb muscles.
- Proprioception exercise and conditioning for normal activity.